In recent years, wearable technology has dramatically evolved from simple step counters and heart rate monitors to sophisticated devices capable of interpreting complex physiological and psychological data. One of the most promising and groundbreaking developments in this field is the emergence of emotion-detecting wearables. These devices are designed to recognize, track, and analyze the wearer’s emotional states in real time, offering an unprecedented opportunity to revolutionize mental health management. This article delves into how these devices work, their applications in mental health, the potential benefits and challenges they bring, and what the future might hold for emotional wearables in transforming psychological wellbeing.
How Do Emotion-Detecting Wearables Work?
Emotion-detecting wearables utilize an array of sensors coupled with artificial intelligence (AI) to monitor physiological signals that correlate closely with human emotions. Unlike traditional wearables that primarily focus on physical metrics, these advanced devices analyze subtle biological and behavioral changes to infer emotional states.
- Heart Rate Variability (HRV): HRV measures the variation in time between heartbeats. A higher variability typically indicates relaxation, whereas lower variability can signal stress or anxiety. Since emotional stress affects autonomic nervous system responses, HRV is a key metric in emotion detection.
- Galvanic Skin Response (GSR): GSR sensors measure the electrical conductance of the skin, which fluctuates with sweat gland activity. Emotional arousal, such as excitement, fear, or anxiety, triggers increased sweat production, leading to higher skin conductance.
- Body Temperature: Emotional states often cause subtle changes in peripheral body temperature. For instance, stress may cause temperature drops in extremities due to vasoconstriction.
- Respiratory Patterns: Changes in breathing rate and depth often accompany different emotions; rapid, shallow breaths can indicate anxiety, while slow deep breaths suggest calm.
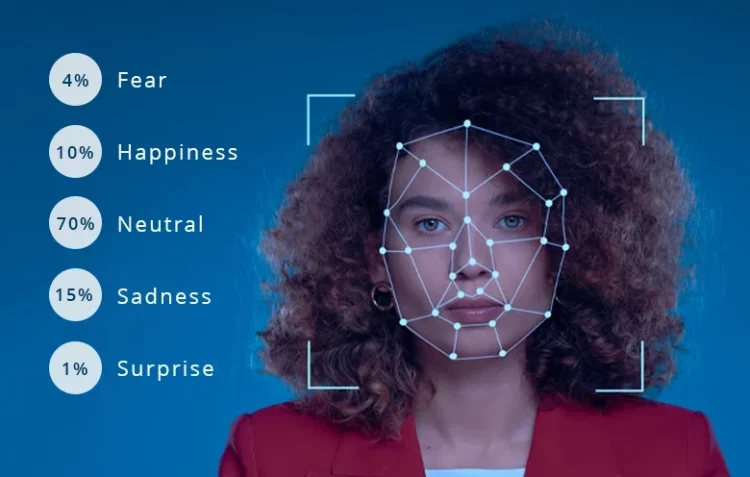
- Facial Expression Recognition: Some wearables, especially smart glasses or companion smartphone apps, use cameras and AI to analyze micro-expressions — brief, involuntary facial movements that reveal underlying emotions.
- Voice and Speech Analysis: AI algorithms can detect emotional cues from voice tone, pitch, speed, and inflection, which often shift according to mood.
By integrating these diverse data streams, emotion-detecting wearables employ sophisticated machine learning models to estimate emotional states such as happiness, sadness, anger, fear, or calmness. Continuous, real-time monitoring allows for a dynamic emotional profile tailored to each user.
Applications in Mental Health Management
The ability to detect emotions accurately and continuously unlocks a variety of powerful applications for mental health care, many of which could drastically improve current treatment models.
Real-Time Mood Monitoring and Early Detection
One of the most valuable uses of emotional wearables is in real-time mood tracking. For individuals struggling with conditions like depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), emotional fluctuations can serve as early warning signs of potential crises. Wearables can detect these mood shifts promptly and alert users or their healthcare providers, enabling early intervention that might prevent severe episodes or hospitalizations.
Personalized Coping Strategies and Interventions
Emotion-aware wearables are capable of not only detecting emotional distress but also offering immediate, personalized interventions. When signs of stress or anxiety are detected, the device can prompt users to engage in relaxation techniques such as guided breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, or cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) modules through a connected app. This real-time support bridges the gap between therapy sessions, providing continuous assistance tailored to individual emotional needs.
Augmented Teletherapy and Clinical Support
For mental health professionals, emotion data from wearables offers invaluable insights into patients’ emotional well-being between clinical appointments. Teletherapy platforms integrated with emotion-detecting devices allow therapists to access objective data on patients’ mood trends, triggers, and responses to treatment. This empowers clinicians to adjust therapy plans more effectively and provide personalized care remotely, improving treatment outcomes.
Stress Management in Daily Life
Beyond clinical settings, emotion-detecting wearables can support stress management for the general population. By providing continuous feedback on emotional states, users become more aware of stressors and their physiological impacts. Over time, this heightened awareness can lead to better lifestyle choices, improved resilience, and healthier emotional regulation.

Potential Benefits of Emotion-Detecting Wearables
The integration of emotion recognition technology into wearables offers numerous benefits that could transform mental health management on multiple fronts.
- Proactive Mental Healthcare: By detecting emotional changes early, these devices enable preventive care that addresses issues before they escalate, reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
- Empowerment and Self-Awareness: Continuous emotional feedback fosters greater self-awareness, empowering users to take an active role in managing their mental health.
- Reduced Stigma: Wearables provide a private, non-intrusive means of monitoring mental health, helping to reduce stigma and encouraging more people to seek help.
- Accessibility: When paired with digital therapeutics and telehealth, these devices can extend quality mental health support to remote or underserved populations.
- Personalization: Emotional data enables highly individualized treatment plans that reflect a person’s unique emotional patterns and triggers.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the promising benefits, several challenges must be addressed to maximize the effectiveness and adoption of emotion-detecting wearables.
Data Privacy and Security
Emotion data is highly sensitive, raising critical concerns about privacy and data protection. Robust encryption, transparent user consent protocols, and strict data governance are essential to safeguard personal emotional information from misuse or breaches.
Accuracy and Reliability
Emotions are complex and influenced by many factors, making accurate detection challenging. False positives (incorrectly identifying distress) or false negatives (failing to detect an episode) could undermine trust in these technologies or cause unnecessary anxiety.
Ethical Implications
The use of emotion detection raises ethical questions about consent, autonomy, and potential misuse—such as employer monitoring or insurance discrimination. Clear guidelines and regulations are needed to ensure ethical deployment.
User Engagement and Accessibility
To be effective, wearables must be comfortable, easy to use, and culturally sensitive. Ensuring affordability and accessibility across diverse socioeconomic groups is also crucial to prevent widening health disparities.
The Future of Emotion-Detecting Wearables in Mental Health
As sensor technology and artificial intelligence continue to advance, emotion-detecting wearables will become increasingly sophisticated, accurate, and integrated into broader healthcare ecosystems. Future developments may include:
- Multimodal Emotion Sensing: Combining physiological, behavioral, and contextual data (like environment and social interactions) to refine emotional detection.
- Integration with Other Health Data: Merging emotional insights with genomic, metabolic, and physical activity data for comprehensive personalized health management.
- Predictive Emotional Modeling: Using AI to forecast emotional states and mental health trajectories, enabling preemptive interventions.
- Enhanced User Interfaces: Employing augmented reality and haptic feedback for more immersive and intuitive emotional support.
- Collaborative Platforms: Connecting patients, caregivers, and clinicians in real-time emotional monitoring and support networks.
These innovations promise to shift mental health care from reactive treatment to continuous, personalized emotional wellbeing management, reducing the global burden of mental illness.
Conclusion
Wearable devices capable of detecting emotions represent a major leap forward in mental health management. By providing real-time, personalized emotional insights and interventions, they have the potential to transform how individuals understand and care for their mental wellbeing. While challenges around accuracy, privacy, and ethics remain, the continued evolution of this technology holds great promise for a future where mental health care is proactive, precise, and accessible to all.